Publications
Research contributions in AI, deep learning, and medical signal processing
Detection of Interictal epileptiform discharges with semi-supervised deep learning
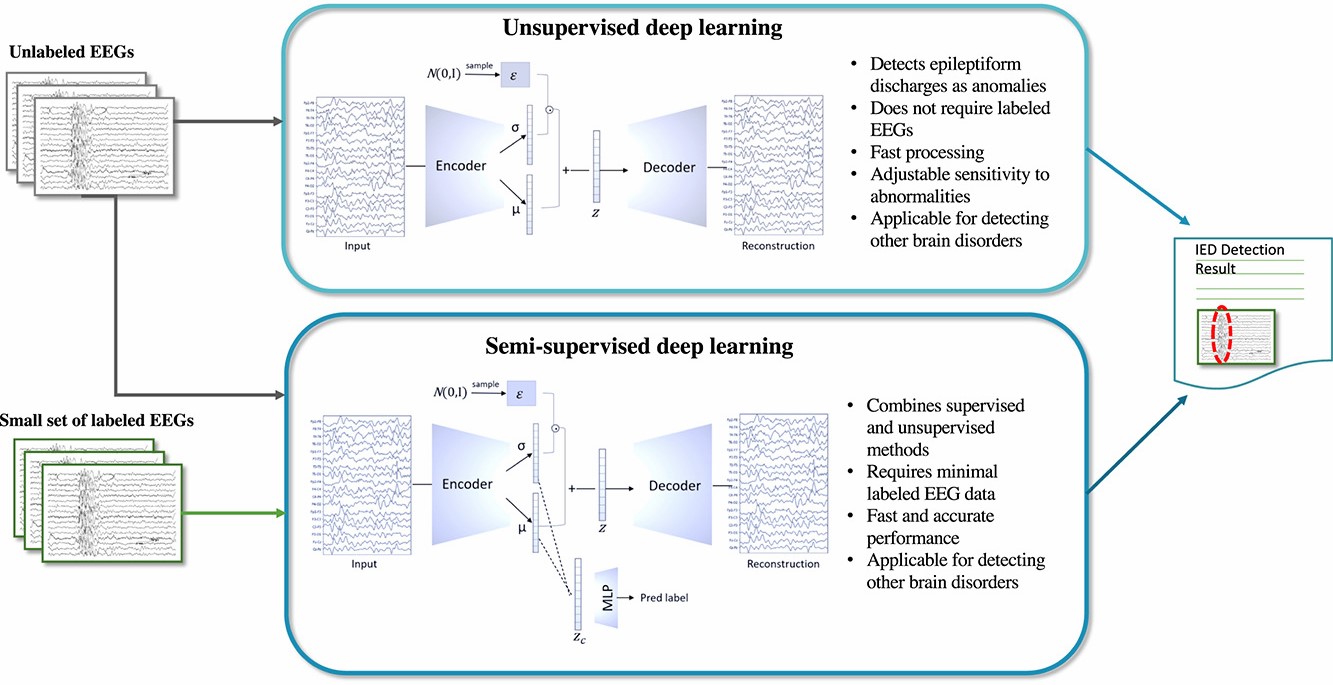
Interictal discharges (IEDs) in EEG recordings are important signatures of epilepsy as their presence is strongly associated with an increased risk of seizures. IEDs are relatively short-duration events (typically 70-250 ms) that can be viewed as stochastic anomalies in such recordings. Currently, visual analysis of the EEG by clinical experts is the gold standard. This process, however, is time-consuming, error-prone, and associated with a long learning period.
Learning to write medical reports from EEG data
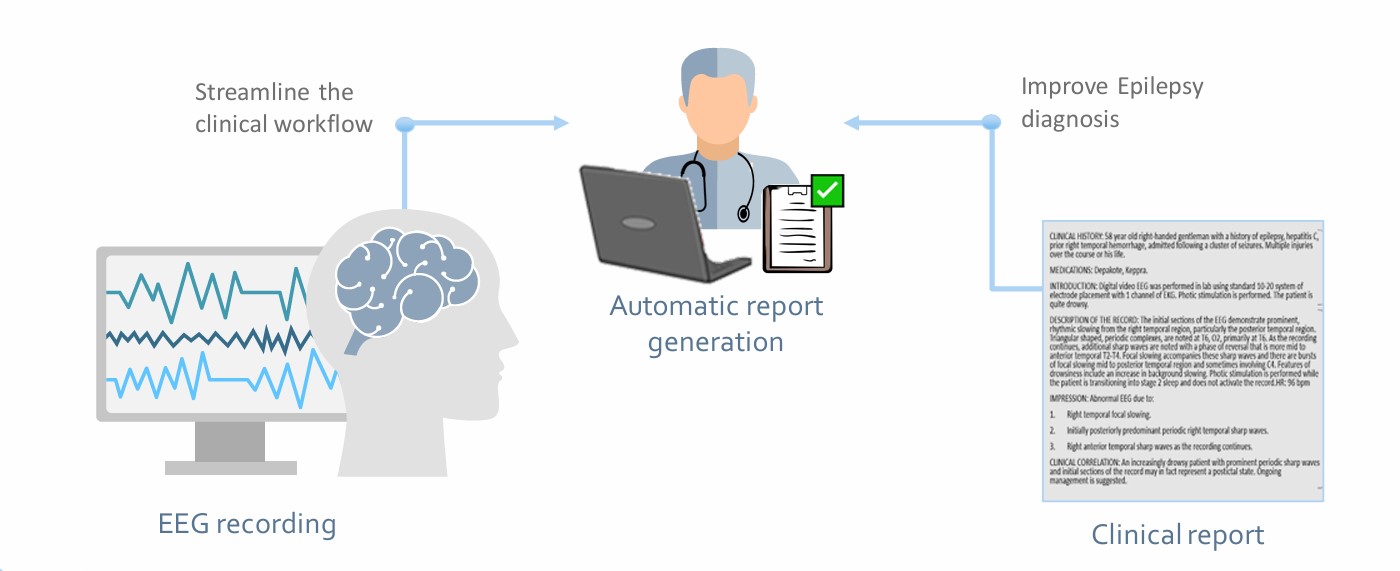
Electroencephalography (EEG) is an essential tool for the diagnosis and management of epilepsy, one of the most prevalent neurological disorders in the world, characterized by an increased likelihood of seizures. However, these periods of abnormal brain activity (ictal EEG) may not occur often, so the diagnosis is usually made by visual analysis of the EEG in interictal periods. During this analysis, the neurologist summarizes the findings and diagnosis in a clinical report. Although this is a current practice, it entails several disadvantages that motivate the development of automatic auxiliary algorithms that can streamline clinical workflow, reduce subjectivity, and potentially improve diagnosis.